Explain How Target Costing Is Different From Cost Plus Pricing
The absorption costing approach to cost plus pricing differs from the economists approach price elasticity of demand both in what costs are marked up and in how markup is determined. Traditional or cost-plus costing has been around for many decades much longer than target costing.
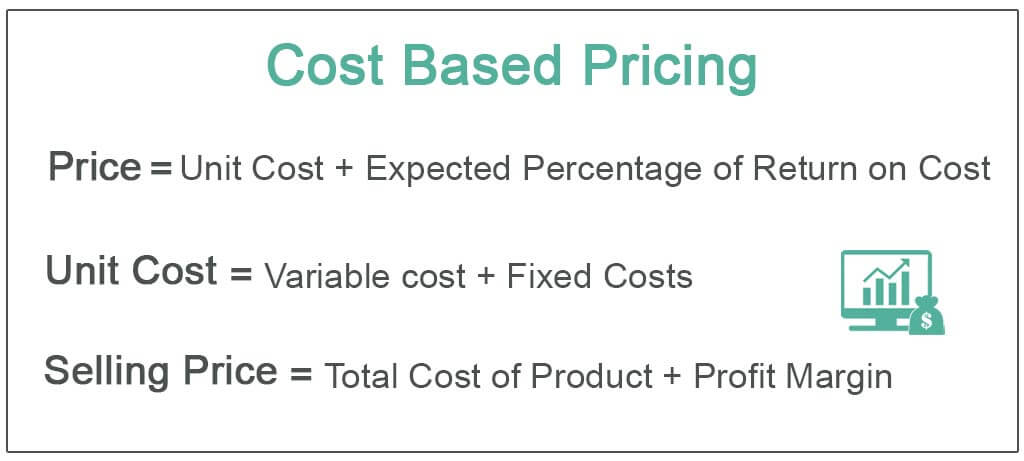
Cost Based Pricing Definition Formula Top Examples
9DQ expand_more Business Accounting Financial And Managerial Accounting Explain the difference between target.
. Differential Analysis And Product Pricing. A target market price is determined by marketing managers before designing and introducing. A number of companiesprimarily in Japan use target costing including Compaq Culp Cummins Engine Daihatsu Motors DaimlerChrysler Ford Isuzu Motors ITT NEC and Toyota etc.
We can also look at cost plus pricing like this. Target Costing is different from standard costing. Many of Japans leading manufacturers such as.
The primary difference between target costing and traditional cost-based pricing is a. Set prices too high and customers walk. Target costing is quite different to cost plus pricing.
Most businesses prefer it. 500 500 x 50 750. Target costing was developed in the 1960s by market and cost researchers working for Toyota.
Ais generally determined after introducing a product and cost-plus pricing is determined before introducing a product. While in Target costing the amount incurred on the product is managed from a predetermined cost for a product. Cost plus pricing is using to identify the direct costs absorb appropriate overheads and gives the selling price.
Answer the following questions regarding the development of the Neon car. Setting inappropriate prices may not be the primary reason that companies are forced to close up shop but its as good a reason as any. Explain how target costing is different from cost plus pricing.
How is it different from a budgeted cost. Explain and give an example of cost-plus pricing target costing and yield management pricing. Sales price at which customers would buy the product is to be set first and then costs would be adjusted which has led to market driven approach to cost accounting.
In product development target costing is a management technique used to determine the cost of manufacturing a product while cost-plus pricing is a system used to determine the selling price of. It is the costing process in which companytries to reduces all costs of product to limit the selling price atspecific targeted selling price. Cost-plus pricing is a methodology in which the selling price of a product is determined based on unit costing by adding a certain mark-up or profit premium to the cost of the product.
This gives a cost per product that satisfies the financial reporting standards for stock valuation and a cost which will cover all the costs involved in getting the product to the condition and location where it is held. Target costing is still most widely practiced in and most closely associated with Japan. The management can determine the desired profit margin.
Explain and give an example of cost-plus pricing target costing and yield management pricing Cost-plus pricing means marketers total all the costs for the product then add an amount to arrive at the selling price. Bis a simple approach while cost-plus pricing is relatively complex. Products with a lot of competition or that are not unique.
A difference in cost-plus pricing and target costing is that target costing. Under the absorption costing approach to cost plus pricing the cost base is the absorption costing unit product cost rather than variable costing. In Cost plus pricing the price of a product is calculated as cost incurred on the product plus profit amount.
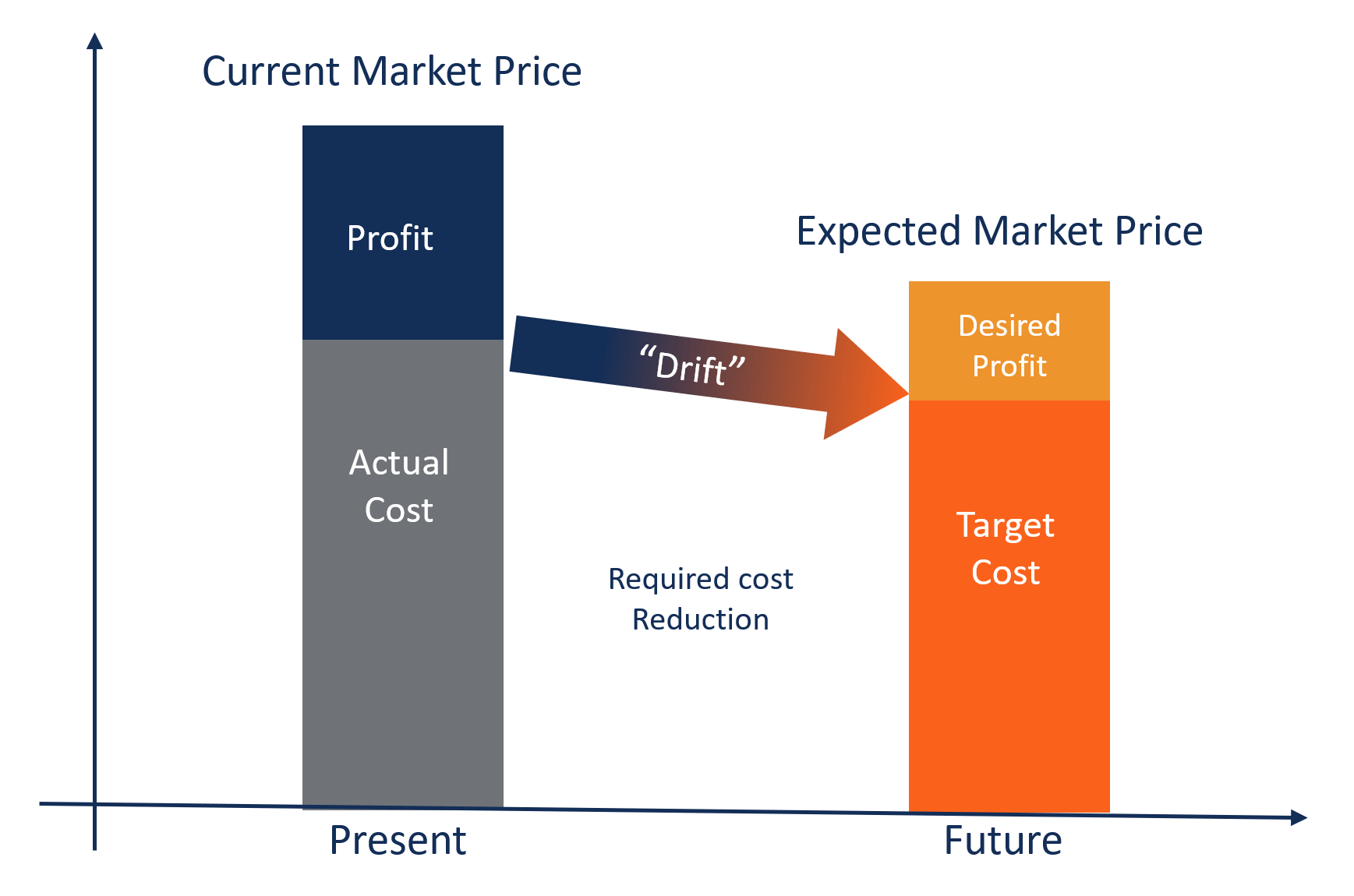
Under the target costing allowable product cost ie. Target costing involves looking at what the company wants for a profit the price for the product that the market will bear and then determines how to potentially cut costs to reach the desired profit. Target cost is derived by conducting market research and predict the target selling price which is willing to pay for the product with specific characteristics.
Target costing An approach to pricing that integrates the product design desired price desired profit and desired cost into one process beginning at the product development stage. Total Costs Desired Profit Desired Revenue. Traditional cost-based pricing is designed to appeal to any customers but target costing targets specific customers.
Then the desired profit margin is subtracted from the predicted target selling price to arrive. Target costing is not just a method of costing but rather a management technique wherein prices are determined by market conditions taking into account several factors such as homogeneous products level of competition nolow switching costs Cost of Goods Manufactured COGM Cost of Goods Manufactured COGM is a term used in managerial accounting that refers to a. 100 per unit for producing a product.
In cost-plus pricing method a fixed percentage also called mark-up percentage of the total cost as a profit is added to the total cost to set the price. Cost plus pricing involves adding a markup to the cost of goods and services to arrive at a selling price. A target cost is the allowable amount of cost that can be incurred on a product and still earn the required.
Under this approach you add together the direct material cost direct labor cost and overhead costs for a product and add to it a markup percentage in order to derive the price of the product. Is an approach that mitigates cost efficiency problems associated with introducing new products by integrating the product design desired price desired profit and desired cost into one process. Cstarts with the price customers are willing to pay whereas cost-plus pricing.
Target costing is influenced by a number of external market factors. For example XYZ organization bears the total cost of Rs. Traditional cost-based pricing considers the market that is available for the product at the end of the process whereas target costing considers the market at the beginning of the.
Target costing is based on marketing factor ie. In simple words it is a strategy of pricing a product in the market by adding a. Set prices too low and your business may be forced to shutter its windows and close its doors.
Target costing is the process of determining the maximum allowable cost for a new product and then developing a prototype that can be profitably made for that maximum target cost figure. While target costs are determined by market driven standards target sales price target profit target cost standard costs are determined by design driven standards with less emphasis on what the market will pay engineered costs desired markup desired sales price.
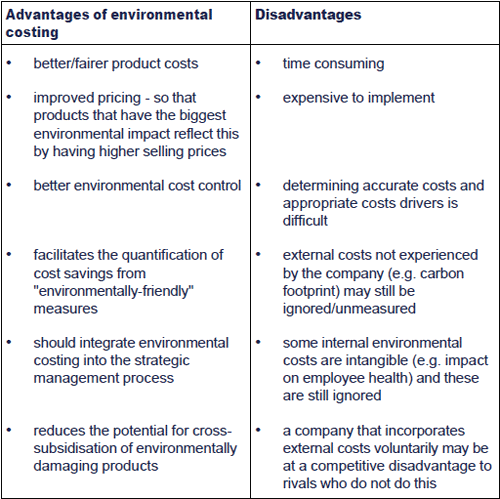
Chapter 1 Traditional And Advanced Costing Methods

Cost Plus Pricing Definition Method Formula Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Obstacles To Implementing Value Based Pricing Imd Article

Target Costing Key Features Advantages And Examples
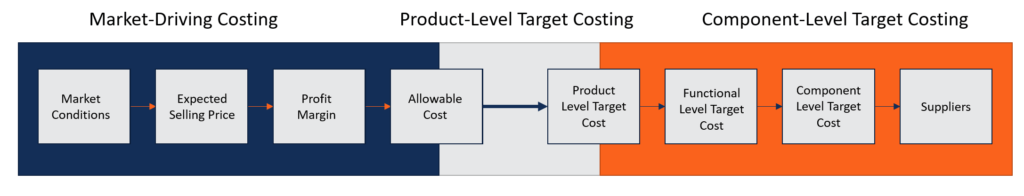
Target Costing Key Features Advantages And Examples
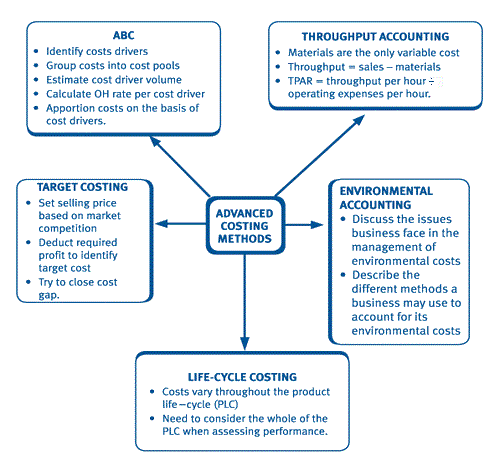
Chapter 1 Traditional And Advanced Costing Methods
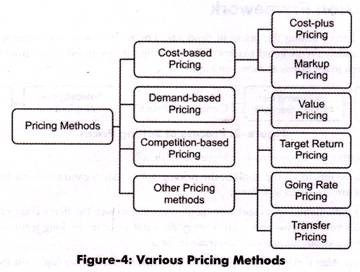
4 Types Of Pricing Methods Explained
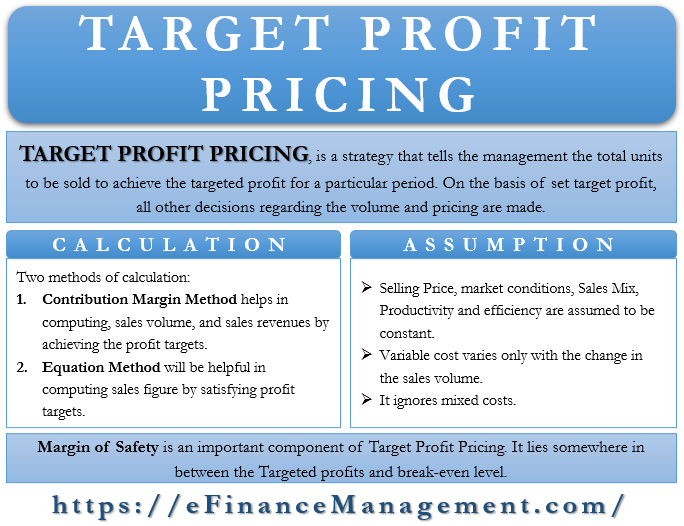
Target Profit Pricing Meaning Methods Assumptions And More Efm

This Video Gave A Good Example Of Price Takers And Price Setters I Found The Examples Given Make It More Relatable Latest Tech Gadgets Relatable Tech Gadgets
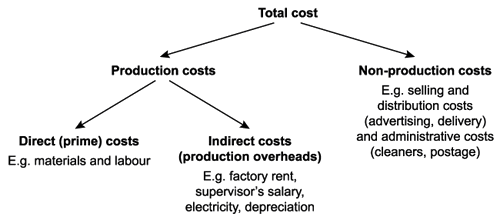
Chapter 1 Traditional And Advanced Costing Methods

Target Costing And Lifecycle Costing Acca Global
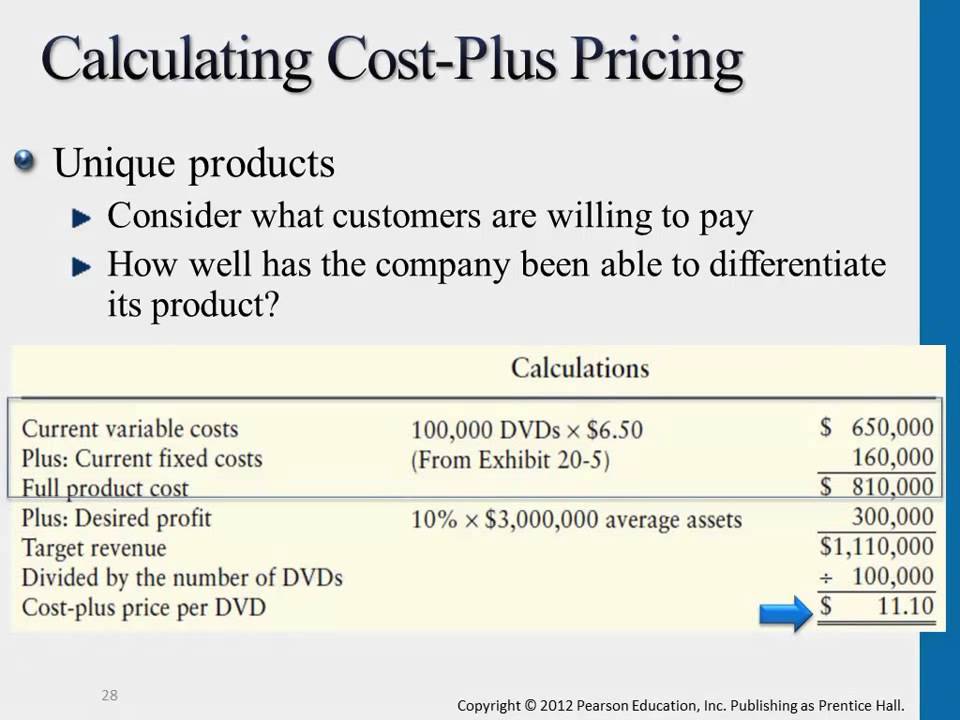
Calculating Cost Plus Pricing Youtube

44 Managerial Accounting 7 7 Cost Plus Pricing And Target Costing Youtube Managerial Accounting Accounting Cost Plus

Target Costing And Lifecycle Costing Acca Global
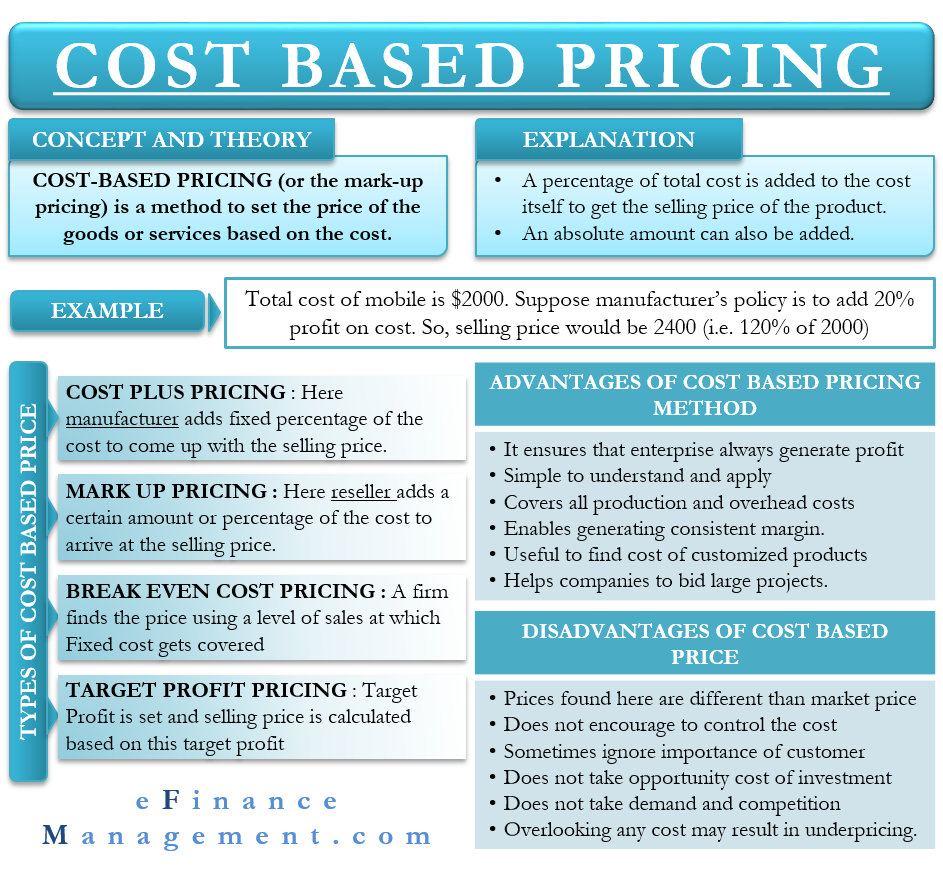
Cost Based Pricing Meaning Types Advantages And More

I Found This Formulae Very Helpful It Shoes Four Different Ways Of Calculating Degree Of Operating Leverag Contribution Margin Financial Management Fixed Cost
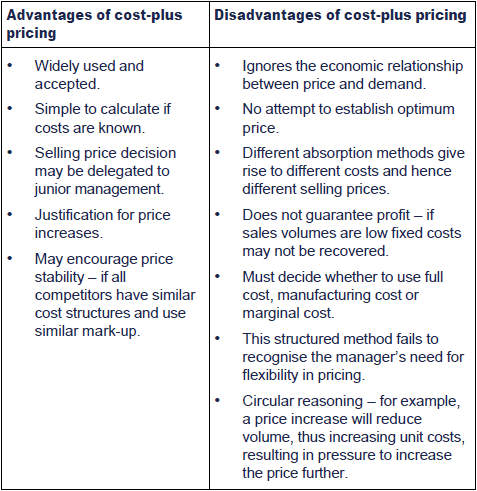

Comments
Post a Comment